How to use object in Kotlin
In Kotlin, object is used when you need a single instance of a class or when defining an anonymous object. Here are the main use cases:
1. Singletons (Object Declarations)
Use object when you need a single instance of a class throughout your application.
2. Companion Objects
Use companion object inside a class to define static-like behavior.
3. Anonymous Objects (Object Expressions)
Use object when you need a one-time implementation of an interface or class.
⚡ Use case: Implementing listeners or callbacks without creating a full class.
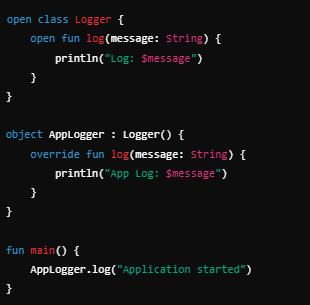
4. Object Inheritance (Using object with a Superclass)
If a singleton needs to extend another class or implement an interface:
⚡ Use case: Creating a global logging instance.
Summary
| Singleton | (object) | Global database manager, configuration, logging |
| Static-like behavior | (companion object) | Factory methods, constants inside a class |
| Anonymous class | (object expression) | Event listeners, callbacks |
| Inheritance | (object with superclass) | Extending abstract classes or implementing interfaces |



Comments
Post a Comment